Designed for sequential data with memory capabilities, ideal for time series, speech recognition, and language modeling.
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to progressively extract higher-level features from raw input.
Unlike traditional machine learning approaches, deep learning models can automatically discover the representations needed for feature detection or classification from raw data, making them incredibly powerful for complex tasks.
Explore the fundamental building blocks and applications of deep learning technology
The foundational architecture inspired by biological neurons, consisting of interconnected layers that process and transform data.
Specialized for processing grid-like data such as images, using convolutional layers to detect spatial hierarchies of features.
Designed for sequential data with memory capabilities, ideal for time series, speech recognition, and language modeling.
State-of-the-art architecture using self-attention mechanisms, powering modern NLP and multi-modal AI systems.
Applications in image classification, object detection, facial recognition, and autonomous navigation systems.
Natural language understanding, machine translation, conversational AI, and intelligent robotic control systems.
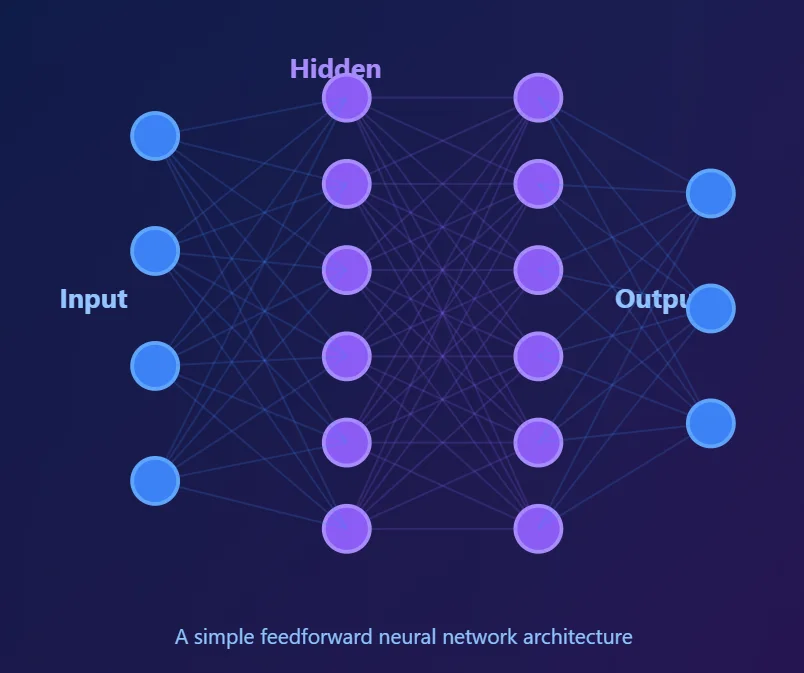
Hover over each layer to explore how deep neural networks process information
nodes
Recieve raw data (images, text audio) and covert into numerical format that the network can process.
nodes
First level of feature extraction, Detects simple patterns like edges, corners, and basic shapes in the data.
nodes
Combines features from previous layer to recognize more complex patterns and higher-level abstractions.
nodes
Deep feature extraction layer that identifies sophisticated patterns and representations from combined features..
nodes
Produces final predictions or classifications. Each neuron represents a possible class or output value.
Comprehensive guides and case studies to accelerate your deep learning journey


Everything you need to know about deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers (hence "deep"). While traditional machine learning often requires manual feature engineering, deep learning models automatically learn feature representations from raw data. Deep learning excels at handling unstructured data like images, audio, and text, making it more powerful for complex tasks.
For beginners, a standard CPU is sufficient for learning concepts and small models. However, for training larger models, a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) dramatically speeds up computation. NVIDIA GPUs with CUDA support are most common. Cloud platforms like Google Colab, AWS, or Azure also offer GPU access without requiring expensive hardware investments.
TensorFlow and PyTorch are the two most popular frameworks. PyTorch is often recommended for beginners due to its intuitive, Pythonic syntax and excellent for research. TensorFlow has strong production deployment capabilities and a larger ecosystem. Both are excellent choices, and many concepts transfer between them.
It varies by task complexity. Simple problems might need hundreds to thousands of examples, while complex tasks like image recognition may require tens of thousands or more. Techniques like transfer learning, data augmentation, and pre-trained models can significantly reduce data requirements by leveraging existing knowledge.
Deep learning powers many modern AI applications: computer vision (facial recognition, autonomous vehicles), natural language processing (chatbots, translation), speech recognition (voice assistants), recommendation systems, medical diagnosis, drug discovery, robotics, game playing, and generative AI (image/text generation).
Training time varies widely based on model complexity, dataset size, and hardware. Simple models might train in minutes on a GPU, while large language models or complex vision systems can take days or weeks on powerful hardware clusters. Modern techniques like distributed training and efficient architectures help reduce training time.
Python is the primary language for deep learning. You should be comfortable with Python basics, NumPy for numerical computing, and basic linear algebra and calculus concepts. Familiarity with libraries like Pandas for data manipulation and Matplotlib for visualization is also helpful. Most importantly, start with projects and learn by doing.
We’re a team of passionate tech writers helping developers, marketers, and privacy-conscious users navigate the digital world. From mobile development to AI and SEO, our goal is to deliver clear, actionable insights.
© 2026, Android Studio Hub. All Rights Reserved.