"Master the art of developing Android applications by learning Kotlin, Jetpack Compose, and scalable architecture with comprehensive hands-on guides, expert tips, and invaluable insights to enhance your skills and boost your projects."



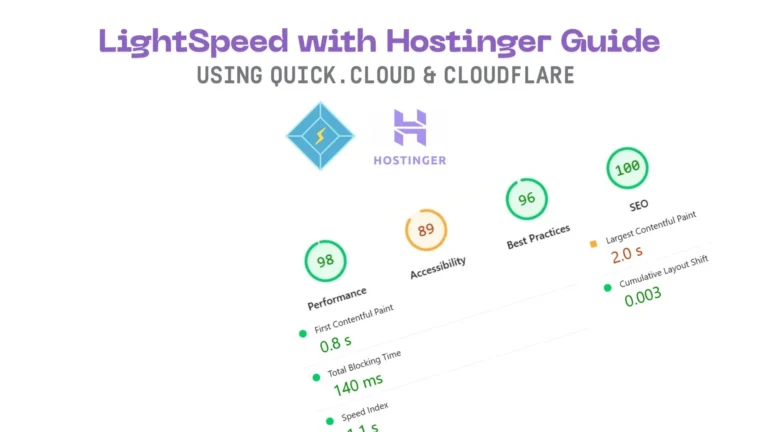




Learn Basics of Kotlin
Basic to Advance design
Basic to Advance
How to test & debug
Explore fresh insights and expert tutorials on Android coding and architecture. From mastering Kotlin and Jetpack Compose to implementing scalable MVVM patterns, these articles help you build robust apps, design intuitive UIs, and debug with confidence.







Create modern, declarative Android interfaces with less code and more flexibility.
Jetpack Compose is Android’s modern UI toolkit. It replaces XML layouts with Kotlin-based declarative components, making UI development faster and more intuitive. Here’s a basic example of a composable function:
@Composable
fun Greeting(name: String) {
Text(text = "Hello $name!")
}
Separate concerns and build scalable apps with ViewModel and LiveData.
MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) helps organize your Android codebase by separating UI logic from business logic. It improves testability and works seamlessly with Jetpack components. Here’s how you define a simple ViewModel:
class MainViewModel : ViewModel() {
val userName = MutableLiveData<String>()
}Kotlin is the preferred language for Android development. Its concise syntax and null safety features make it ideal for building robust apps. Here’s a simple function that prints a greeting:
fun greetUser(name: String) {
println("Hello, $name!")
}Logcat is a powerful tool for tracking runtime behavior and diagnosing issues in Android apps. Use it to print debug messages and monitor app flow. Here's a basic usage example:
Log.d("MainActivity", "App started successfully")To use Jetpack Compose, you need to enable it in your Gradle configuration. This snippet activates Compose features in your module-level build.gradle file:
buildFeatures {
compose true
}MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) is widely recommended for Android apps. It separates UI logic from business logic, improves testability, and works seamlessly with Jetpack libraries like LiveData and ViewModel.
Use modular packages for UI, data, domain, and core utilities. Follow clean architecture principles and keep your Gradle files organized with buildSrc or version catalogs.
MVVM uses reactive data-binding and ViewModels, while MVP relies on manual presenter logic. MVVM is more modern and integrates better with Jetpack Compose and LiveData.
Enable configuration caching, use parallel execution, avoid unnecessary plugins, and keep dependencies up-to-date. Tools like Gradle Profiler can help identify bottlenecks.
Kotlin is now the preferred language for Android development. It offers concise syntax, null safety, and full support from Google. Java is still supported but less modern.
Jetpack Compose is Android’s modern UI toolkit. It simplifies UI development with declarative syntax, reduces boilerplate, and integrates tightly with Kotlin and Android Studio.
Use Logcat, breakpoints, and the Android Profiler. Tools like LeakCanary and Firebase Crashlytics help catch memory leaks and runtime crashes. Always test on real devices.
For activities: onCreate(), onStart(), onResume(), onPause(), onStop(), and onDestroy(). Understanding these helps manage resources and UI state efficiently.
Use ViewModel to retain data across configuration changes. Avoid storing UI state in activities or fragments. Consider using savedInstanceState for transient data.
Follow Material Design guidelines, use responsive layouts, test on multiple screen sizes, and prioritize accessibility. Jetpack Compose makes adaptive UI easier to implement.
We’re a team of passionate tech writers helping developers, marketers, and privacy-conscious users navigate the digital world. From mobile development to AI and SEO, our goal is to deliver clear, actionable insights.
© 2026, Android Studio Hub. All Rights Reserved.